Wear pot test
Wear pot test
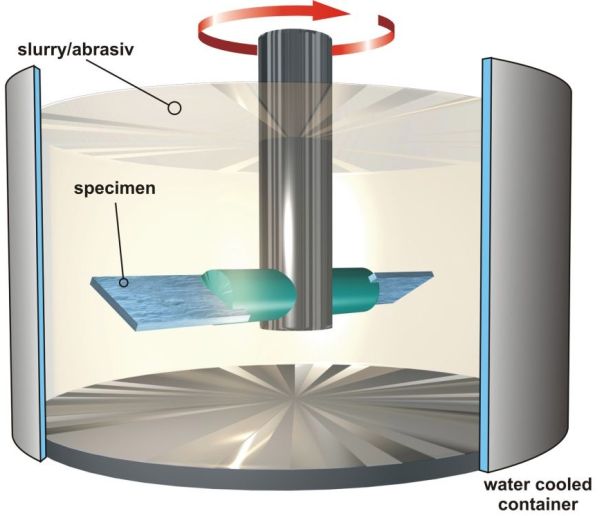
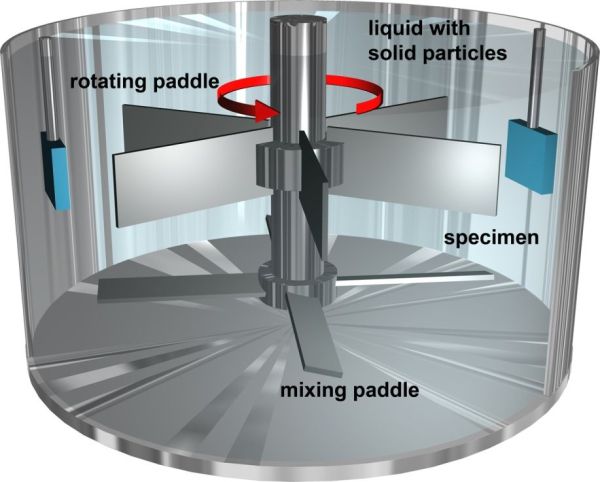
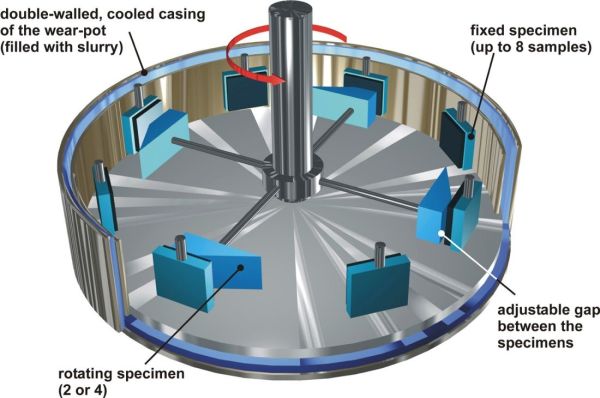
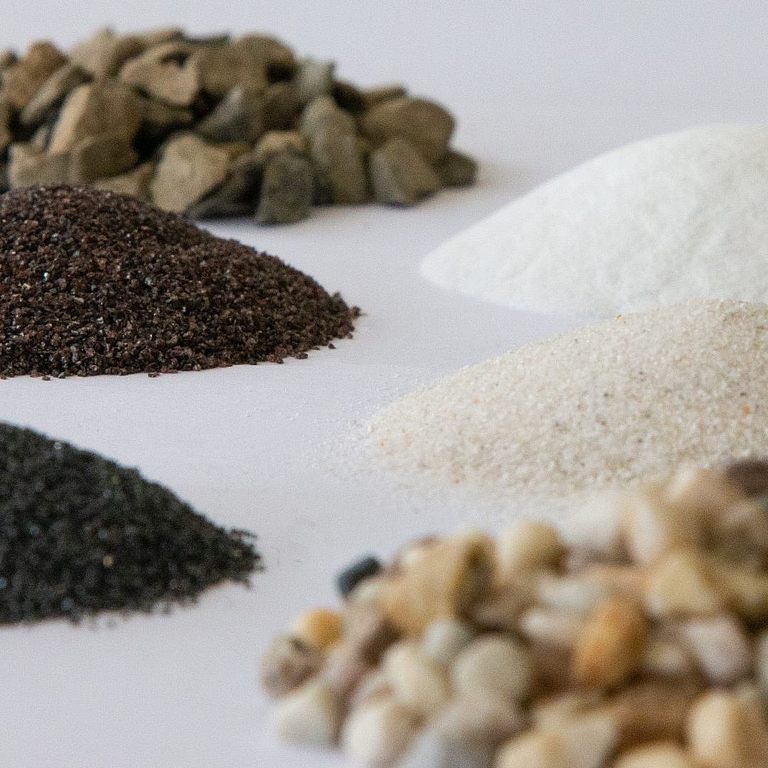
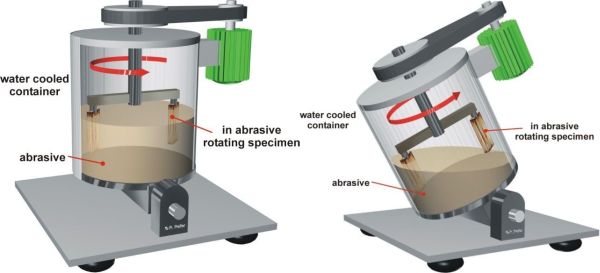
Wear pot tests are two-body abrasive wear. Depending on the liquid content, an erosive or abrasive wear attack is shown. Three wear pots of different sizes (10 to 200 litre capacity) are available at ISAF for the test, with which highly abrasive wear attacks can be simulated. A wide range of achievable speeds, almost free choice of abrasive type, size and composition - also multimodal - and freedom in the test piece geometry allow tribosystem-compatible wear investigations, especially in the following areas
- general apparatus and mechanical engineering
- Separation and filter technology
- Raw material extraction and processing
- Conveying technology
- Building materials industry
- Earth-moving and earth-moving machinery
- Mining, deep drilling technology
- Agricultural soil cultivation
- technical knives e.g. for agricultural engineering etc.
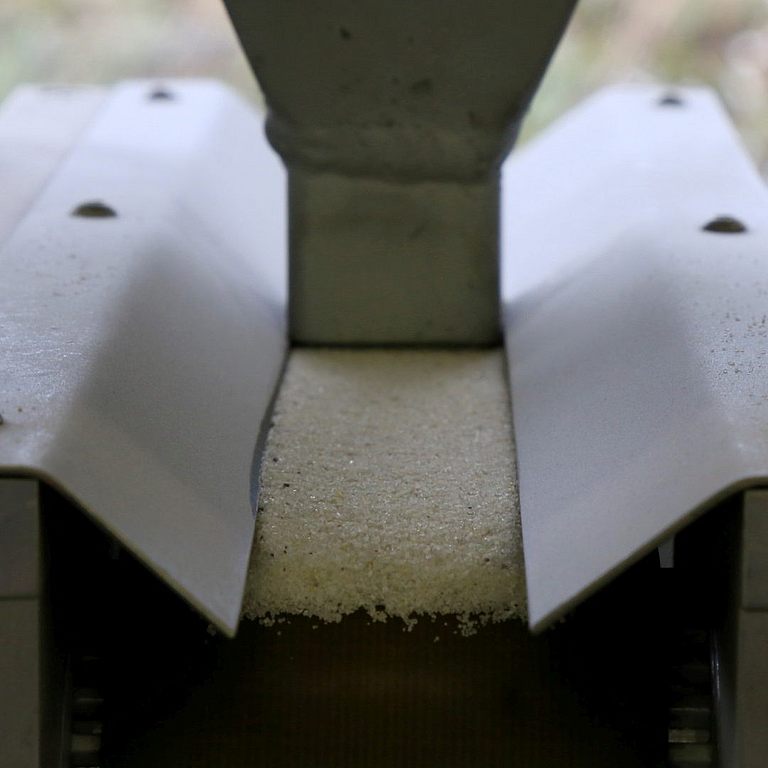
The stress angle is also freely selectable and depends on the respective application. The wear pot method is used to test wear with loose grain. Here, the samples applied to a rotor are driven through a solid-fluid mixture, Figs. 1 to 3. Due to the high mobility of the fluid, the samples must be rigidly mounted in the case of the process variant with a high fluid content in order to ensure sufficient relative movement between sample and mixture, Fig. 2. Depending on the mixing ratio of the mixture and fluid, abrasive-erosive or erosive-corrosive wear occurs on the samples. ISAF offers a wide range of possibilities for both the selection of solids and fluids, such as testing with pasty masses, etc., Figure 3, including tests with basic or acidic, i.e. corrosive, intermediate media. The specimens can be placed at different angles to simulate a user-specific angle of incidence. In the case of the largest wear pot, it is also possible to represent an abrasive, impacting wear attack by tilting the pot; Figure 4. All three pots can be tempered and their speed and test duration can be adjusted.